Helping you find comfort peace of mind
Personalized Mental Health Care Rooted in Compassion, Trust, and Expertise
120M+ individuals are covered by insurance







120M+ individuals are covered by insurance







Welcome to Hope Wellness Center
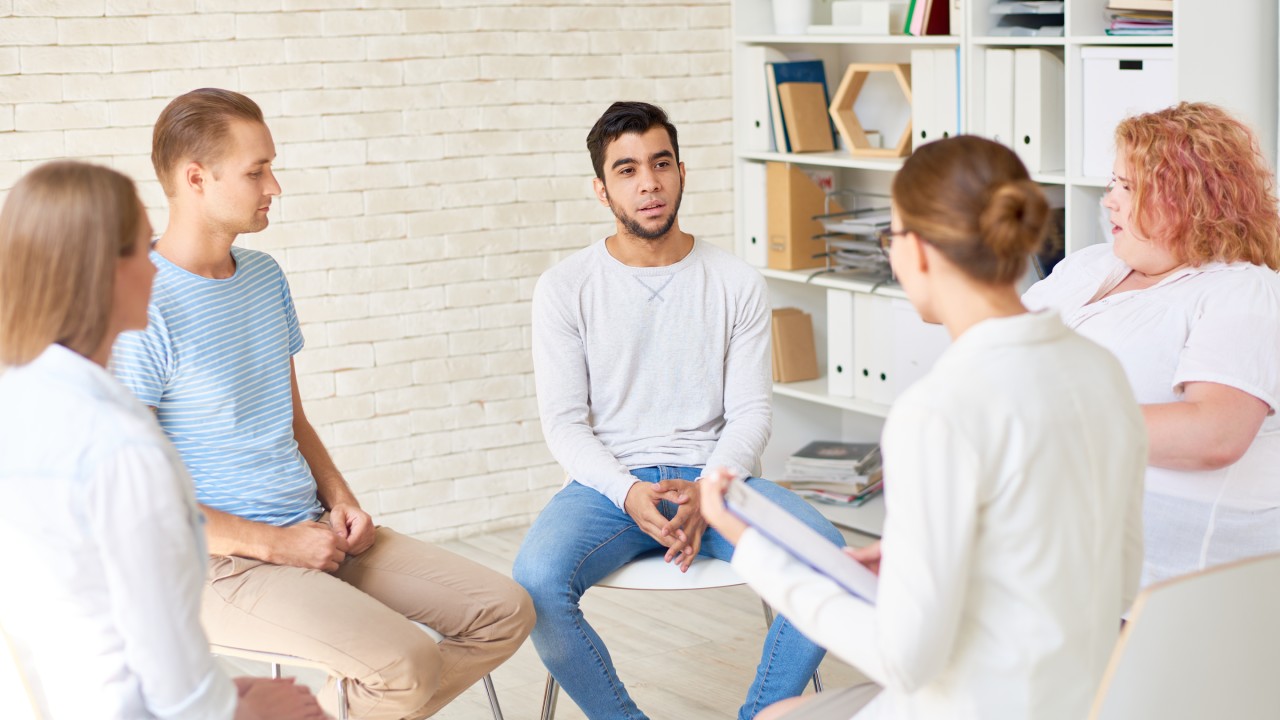
At Hope Wellness Center, we believe in delivering more than just mental health care – we provide a lifeline to comfort, peace of mind, and hope for our community. Our team of compassionate, experienced providers is dedicated to understanding your unique needs and offering personalized, evidence-based treatments that empower you to live your best life.
We’re not just another telehealth service. As local experts deeply invested in the well-being of our community, we bring a personal touch to every interaction, ensuring you feel heard, understood, and supported every step of the way.
Why Choose Hope Wellness Center?
Personalized Care
Local Expertise
Innovative Solutions
Compassionate Team
Affordable Access
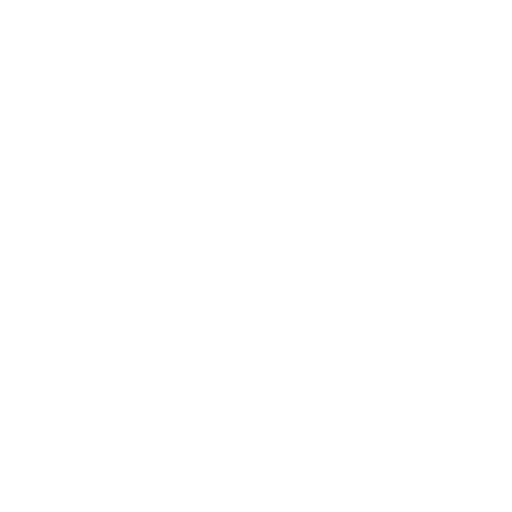
Our Services
Whether you’re seeking therapy, medication management, or specialized care, we’re here to help. At Hope Wellness Center, we offer a wide range of services designed to address your mental health challenges and guide you toward lasting well-being
 Psychotherapy & Counseling
Psychotherapy & Counseling
 Psychotherapy & Counseling
Psychotherapy & Counseling
 Medication Management
Medication Management
 Medication Management
Medication Management
 Behavioral Health Services
Behavioral Health Services
 Behavioral Health Services
Behavioral Health Services
 Substance Abuse Treatment
Substance Abuse Treatment
 Substance Abuse Treatment
Substance Abuse Treatment
 Genetic Testing for Medication Optimization
Genetic Testing for Medication Optimization
 Genetic Testing for Medication Optimization
Genetic Testing for Medication Optimization Advanced tools to find the right medications for you.
Real Stories, Real Results
Your success is our greatest reward. At Hope Wellness Center, we’re proud to be part of so many inspiring stories of resilience and recovery. Ready to start your own success story?



Take the first step today
You don’t have to navigate your mental health journey alone. Hope Wellness Center is here to provide the guidance, support, and care you need to achieve lasting wellness.