ADHD Treatment: Personalized Solutions for Focus, Balance, and Success
At Hope Wellness Center, we understand how challenging living with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) can be. From staying focused to managing daily responsibilities, ADHD can significantly impact your work, education, and relationships.
Our ADHD treatment services are designed to provide personalized, evidence-based care that addresses your unique needs. Whether you’re seeking strategies for improved focus, emotional regulation, or better time management, we’re here to help you regain control and unlock your full potential.
What Is ADHD?
ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. These symptoms can vary in severity and often interfere with daily life, productivity, and interpersonal relationships.
It affects both children and adults, though symptoms may present differently by age.
ADHD often coexists with other conditions like anxiety, depression, and learning disabilities.
Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve outcomes.
Common Symptoms of ADHD
Inattention Symptoms
Difficulty staying focused on tasks or activities.
Frequently losing items like keys, wallets, or homework.
Struggling to follow through on instructions or complete projects.
Hyperactivity Symptoms
Feeling restless or unable to stay seated.
Fidgeting, tapping, or talking excessively.
Difficulty engaging in quiet activities.
Impulsivity Symptoms
Interrupting others or blurting out answers.
Acting without thinking through consequences.
Difficulty waiting for your turn in conversations or activities.
If these symptoms sound familiar, you may benefit from a professional evaluation to determine if ADHD is the root cause.
Our Comprehensive ADHD Treatment Approach
At Hope Wellness Center, we take a holistic and personalized approach to ADHD care.
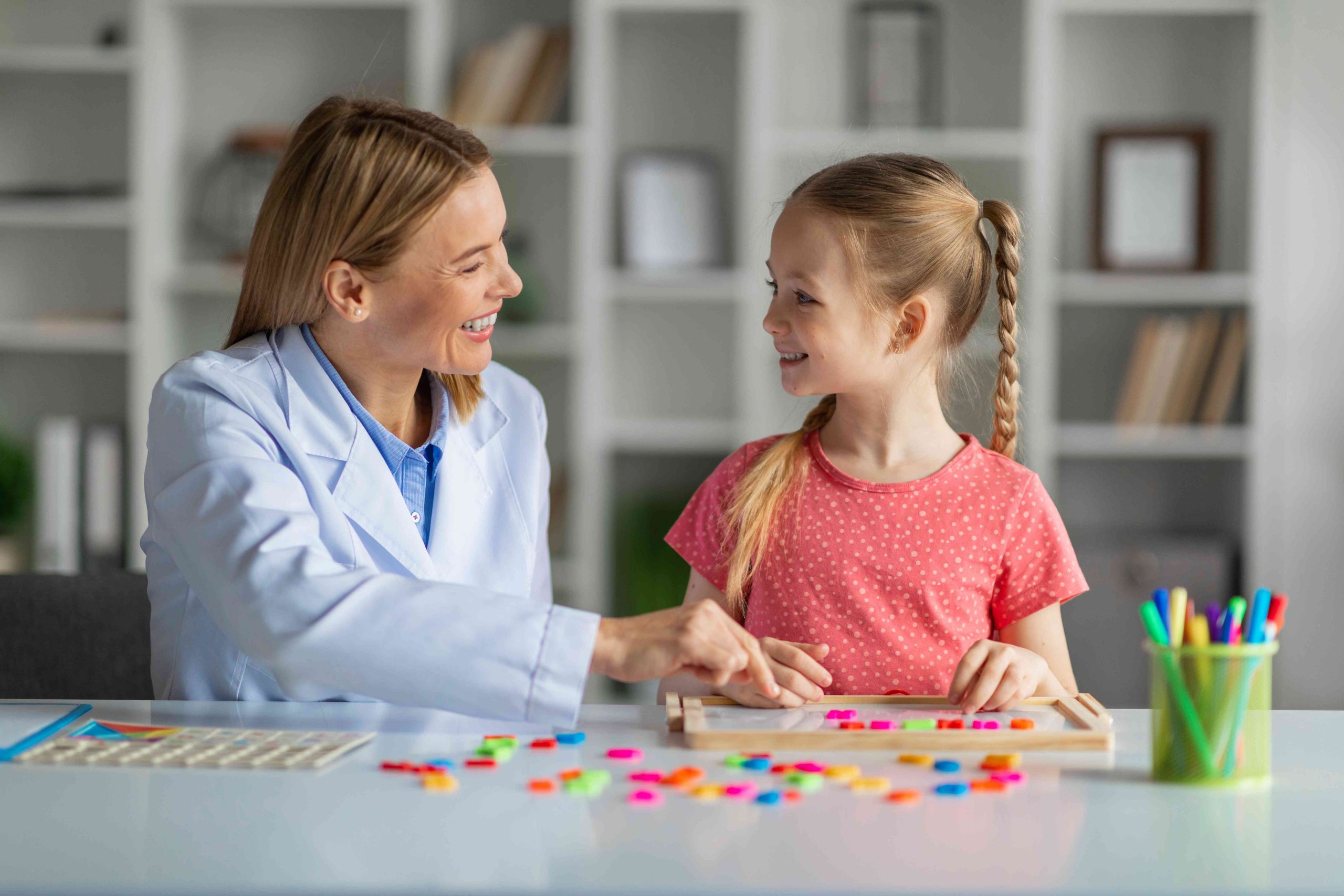
Step 1: Comprehensive Evaluation
Our diagnostic process is thorough, ensuring an accurate understanding of your condition:
Initial Consultation
Discuss your history, symptoms, and daily challenges.
Standardized Testing
Utilize evidence-based tools and questionnaires.
Behavioral Observations
Assess patterns to inform treatment recommendations.
Step 2: Personalized Treatment Plans
Medication Management
Prescribing FDA-approved medications like stimulants or non-stimulants to improve focus and reduce impulsivity.
Regular follow-ups to monitor effectiveness and adjust dosages as needed.
Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) to develop coping strategies and improve self-regulation.
Skills training for time management, organization, and communication.
Lifestyle Recommendations
Strategies for improving sleep, diet, and exercise to support brain health.
Techniques for managing distractions and creating productive routines.
The Benefits of ADHD Treatment
With the right care, individuals with ADHD can achieve significant improvements in their daily lives, including:
Increased Focus and Productivity
Gain the tools needed to complete tasks efficiently.
Better Emotional Regulation
Manage frustration, impulsivity, and mood swings.
Improved Relationships
Communicate effectively and build stronger connections.
Enhanced Self-Esteem
Overcome challenges and celebrate your successes.
Who Can Benefit from ADHD Treatment?
ADHD treatment is valuable for individuals of all ages, including:
Children and Adolescents
Struggling with academics, social interactions, or emotional regulation.
Adults
Facing difficulties with work performance, relationships, or daily responsibilities.
Parents and Families
Learning how to support loved ones with ADHD effectively.
Why Choose Hope Wellness Center for ADHD Treatment?
Expert Providers
Our team specializes in ADHD diagnosis and treatment, offering compassionate care at every step.
Tailored Approaches
We design treatment plans based on your unique symptoms, needs, and goals.
Holistic Care
Integrating medication, therapy, and lifestyle strategies for comprehensive support.
Ongoing Support
We’re committed to helping you succeed long-term, providing regular follow-ups and adjustments.

FAQs About ADHD Treatment
How do I know if I have ADHD?
Can ADHD be treated without medication?
How long does treatment take?
Is ADHD treatment covered by insurance?
Can adults develop ADHD?
Take the first step today
You don’t have to navigate your mental health journey alone. Hope Wellness Center is here to provide the guidance, support, and care you need to achieve lasting wellness.